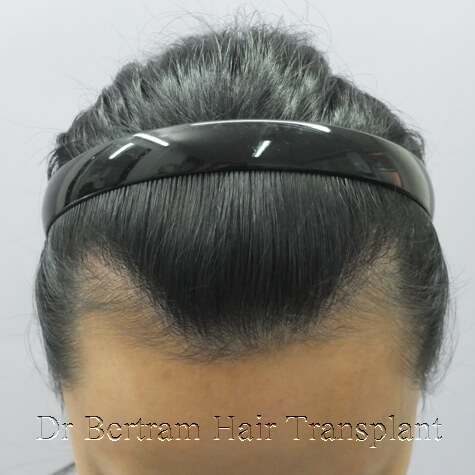
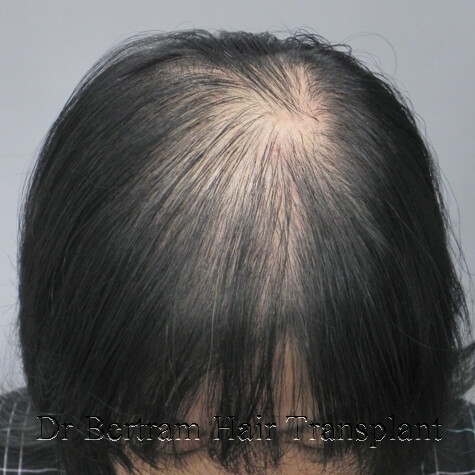
female hair loss - 3 major patterns
Female Pattern Hair Loss (FPHL) is a form of androgenetic alopecia with a multi-factorial, genetically determined trait. Both androgen-dependent and androgen-independent mechanisms plus a biologically normal aging process is involved. Female and male members of the family may both be affected.
Majority has normal type II 5-α reductase levels and normal DHT level in scalp skin. Elevated androgen level were
seen in 16% of women with hair loss alone, and 79% if associated with hirsutism or menstrual disturbance. Though not as common, men can have Female Pattern Hair Loss when thinning extends from the centerline sideway.
3 major patterns in female Pattern Hair Loss
Type 1. M-Shaped or high forehead - Norwood's Classification
Type 2. Thinning at the centerline, extending sidway - Ludqig's or Centrifugal Classification
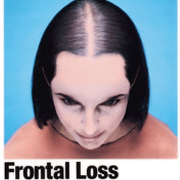
Type 3. Christmas Tree Pattern - Olsen's Classification
Type 1 : Norwood's Classification
• Born with a high forehead or M-shaped hairline
• Thinning of the hairline and the crown similar to men with aging
• Classification is by the Norwood System similar to men

Type 2: Ludwig's Classification
• Central and possibly lateral thinning with sparing of the hairline
• Classification is by the Ludwig System
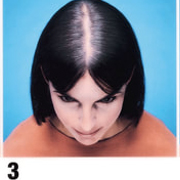
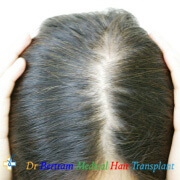
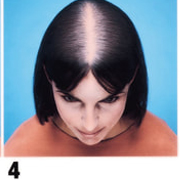
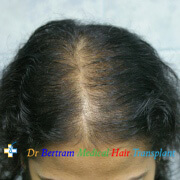
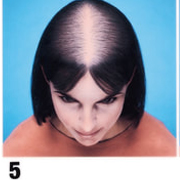
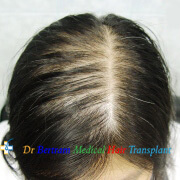
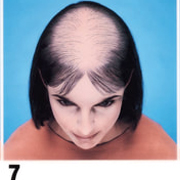

Type 3: Olsen's Classification
• Accentuation of frontal Loss breaching the frontal hairline
• The loss is widest in front tapering towards the crown
• Classification is by the Olsen's System

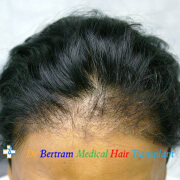

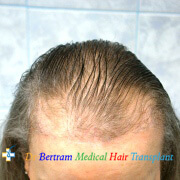
Message from the Doctor
Welcome to “Doctor's Talk,” where I’ll talk about everything related to hair loss and hair transplants. This series is here to help you understand more about how hair treatments work and what you can expect from them. The information provided is based on my 18 years of experience in dealing with hair loss.
Disclaimer -
Please note that this series is purely educational. Reading these posts does not guarantee my services, nor are they intended for business promotion. Information provided is not guaranteed to be up-to-date and should not be considered a substitute for professional medical advice.
Any opinions discussed may not be universally accepted or applicable to all individuals. Always consult a healthcare professional before making any decisions related to your health.

